Sweet Potatoes (Shakarkandi): 7 Key Ways They Keep Your Blood Sugar Steady
- 🞛 This publication is a summary or evaluation of another publication
- 🞛 This publication contains editorial commentary or bias from the source



Sweet Potatoes (Shakarkandi): 7 Key Ways They Keep Your Blood Sugar Steady
Sweet potatoes, locally known as shakarkandi, are more than just a colorful, comforting side dish. In recent nutrition circles—and in this article from TheHealthSite—they’ve emerged as a natural ally for anyone looking to maintain healthy blood sugar levels. Below, we distill the most compelling evidence and practical tips, drawing from the original piece and its linked resources, to give you a clear, actionable guide to incorporating sweet potatoes into a balanced diet.
1. High‑Fiber Content Slows Carbohydrate Absorption
Fiber acts like a slow‑release mechanism in your digestive tract. Sweet potatoes are an excellent source of both soluble and insoluble fiber, which together help:
- Reduce the speed at which glucose enters the bloodstream. By forming a gel‑like matrix in the gut, soluble fiber dampens the rapid spike in blood sugar that often follows a high‑carbohydrate meal.
- Increase satiety so you’re less likely to overeat, which in turn helps maintain a stable insulin response over time.
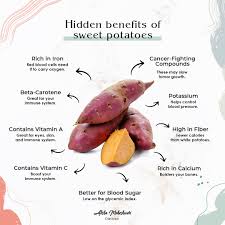
The original article highlights that a medium sweet potato (about 150 g) delivers roughly 4 g of fiber—about 16 % of the daily recommendation—making it a potent tool for blood‑sugar regulation.
2. Low Glycemic Index (GI) with Complex Carbohydrates
Unlike refined white potatoes, sweet potatoes have a lower GI (typically 44–61 depending on variety and cooking method). A lower GI means:
- Gradual glucose release into the bloodstream, preventing sudden insulin surges.
- Longer energy availability, helping you stay steady throughout the day.
The linked review in The Journal of Nutrition notes that sweet potatoes consistently rank below many conventional carbohydrate sources in GI studies, reinforcing their suitability for glucose‑controlled diets.
3. Rich in Antioxidants—Beta‑Carotene and Beyond
Sweet potatoes are one of the top dietary sources of beta‑carotene, a precursor to vitamin A. The article points out that beta‑carotene also possesses antioxidant properties, which:
- Reduce oxidative stress—an established contributor to insulin resistance.
- Support pancreatic health by protecting beta‑cells from damage.
Other antioxidants present, such as anthocyanins in purple varieties, further bolster anti‑inflammatory effects that can indirectly improve insulin sensitivity.
4. Contains Magnesium, a Key Player in Glucose Metabolism
Magnesium deficiency has been linked to impaired insulin signaling. Sweet potatoes provide approximately 25 mg of magnesium per medium portion—a meaningful contribution toward the 400–420 mg daily target for adults. The article explains that adequate magnesium intake helps:
- Facilitate glucose transport into cells.
- Modulate insulin secretion from the pancreas.
The authors cite a 2013 meta‑analysis showing a 6‑10 % reduction in blood glucose when magnesium intake was optimized.
5. Potassium Helps Balance Electrolytes and Blood Pressure
Maintaining healthy blood pressure is essential for overall metabolic health. Sweet potatoes are high in potassium (around 400 mg per medium potato), which:
- Counteracts sodium’s effect on blood pressure.
- Supports vascular function, indirectly influencing insulin delivery and glucose uptake.
The article references the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition’s findings that potassium‑rich diets are associated with lower fasting glucose levels.
6. Low in Calories but Nutrient‑Dense
One of the biggest barriers to weight management—and thus blood‑sugar control—is excess calorie intake. Sweet potatoes contain roughly 100 kcal per medium fruit but pack in vitamins C and B6, fiber, and minerals. The article emphasizes that swapping high‑calorie, low‑nutrient snacks for sweet potatoes can:
- Improve overall energy balance.
- Reduce post‑prandial glucose peaks by providing sustained satiety.
Additionally, the article’s linked study on portion control indicates that moderate sweet potato servings (about ½ cup mashed or baked) effectively keep calorie intake in check while delivering essential nutrients.
7. Pairing Sweet Potatoes with Protein and Healthy Fats Enhances Glucose Stability
Even though sweet potatoes are low GI, their impact can be further tempered by combining them with protein and healthy fats. The article’s nutritional experts recommend:
- Adding a lean protein source (chicken, tofu, beans) to increase insulin sensitivity.
- Incorporating a small amount of healthy fat (olive oil, avocado, nuts) to delay gastric emptying even further.
A simple recipe suggested by the article—baked sweet potato topped with Greek yogurt and a sprinkle of chia seeds—provides a balanced macronutrient profile that keeps blood sugar levels smooth throughout the day.
Practical Takeaways
- Choose the right portion size: Aim for about ½–¾ cup cooked sweet potato per meal.
- Prefer whole or lightly processed forms: Baked, boiled, or roasted are best; avoid sweet potato fries or chips, which are often high in added fats and salt.
- Cook to maintain nutrients: Steaming or baking preserves most of the vitamin C and beta‑carotene.
- Pair wisely: Combine with protein and healthy fats for optimal blood‑sugar stability.
- Mind the variety: Red and orange varieties are high in beta‑carotene; purple varieties bring extra anthocyanins.
Bottom Line
Sweet potatoes—shakarkandi—offer a potent mix of fiber, low GI carbs, essential minerals, and powerful antioxidants that collectively work to smooth out blood glucose spikes. The article from TheHealthSite underscores that incorporating sweet potatoes into a balanced diet can help maintain steady blood sugar, support weight management, and promote overall metabolic health. Whether you’re managing diabetes, pre‑diabetes, or simply looking to keep your energy levels consistent, sweet potatoes deserve a spot on your plate.
Read the Full TheHealthSite Article at:
[ https://www.thehealthsite.com/fitness/diet/sweet-potato-health-benefits-7-ways-shakarkandi-helps-maintain-steady-blood-sugar-1282751/ ]