New FEMA Flood Map Reveals Millions More at Risk
Locales: California, Florida, New York, Texas, Louisiana, UNITED STATES
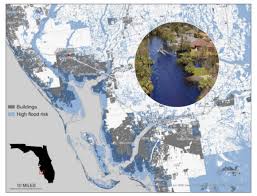




Scale of the Expanding Threat
The map demonstrates a significant expansion of areas designated as high-risk flood zones. While previous maps provided a baseline understanding, they often underestimated the compounding effects of climate change. The new data indicates that millions more properties - both residential and commercial - are now vulnerable to flooding. This expanded risk isn't geographically isolated; it impacts communities along the Atlantic, Gulf, and Pacific coasts, as well as inland areas susceptible to storm surge and riverine flooding exacerbated by rising sea levels. Preliminary analyses suggest areas previously considered 'safe' are now routinely experiencing 'nuisance flooding' during high tides, and are increasingly susceptible to catastrophic damage from major storms.
The Climate Change Catalyst
The defining feature of this updated map is its acknowledgment of climate change as a primary driver of increased flood risk. For decades, FEMA maps largely relied on historical data, assuming a relatively static climate. This approach is no longer viable. Rising global temperatures are contributing to thermal expansion of ocean water and the melting of glaciers and ice sheets, leading to sea-level rise. Simultaneously, warmer ocean temperatures are fueling more powerful hurricanes and nor'easters, capable of generating more intense storm surges and heavier rainfall. The FEMA map attempts to model these complex interactions, offering a more realistic and sobering assessment of future risks. Scientists have long warned about these effects, and this map serves as a visual confirmation of those predictions.
Economic and Insurance Implications
The expanded flood zones will have significant economic consequences. Homeowners and businesses within these zones will likely see substantial increases in flood insurance premiums. In some areas, insurance may become prohibitively expensive or even unavailable, potentially leading to a decline in property values and hindering economic development. Lenders are also likely to factor flood risk into their lending decisions, potentially making it more difficult for individuals and businesses to secure financing. The increased demand on the National Flood Insurance Program (NFIP) could strain its resources, potentially necessitating reforms or even federal bailouts. A vicious cycle could emerge, where rising insurance costs displace residents, further depressing property values and eroding the tax base of coastal communities.
Local Action: A Call to Resilience
FEMA is emphasizing that the map isn't merely a warning, but a call to action for local governments and communities. The agency is urging proactive planning and investment in mitigation strategies. These include a variety of approaches:
- Structural Defenses: Building and reinforcing seawalls, levees, and other protective structures.
- Natural Infrastructure: Restoring and protecting wetlands, mangroves, and other natural ecosystems that provide a buffer against storm surge and erosion.
- Improved Drainage Systems: Upgrading stormwater infrastructure to handle increased rainfall and runoff.
- Elevating Structures: Raising homes and businesses above predicted flood levels.
- Managed Retreat: In some cases, strategically relocating communities away from the most vulnerable areas.
Beyond infrastructure, FEMA stresses the importance of public education. Residents need to understand their flood risk, learn how to prepare for flooding events, and take steps to protect their properties. Community workshops, online resources, and early warning systems are all critical components of an effective flood preparedness program.
Looking Ahead: The Future of Coastal Life
The updated FEMA flood map is a stark reminder of the challenges facing coastal communities. While the news is undoubtedly concerning, it also presents an opportunity for proactive planning and investment in resilience. Ignoring the risks will only exacerbate the problem, leading to greater economic losses and potential loss of life. The map demands a shift in thinking, from reacting to floods after they occur to actively preparing for and mitigating future risks. It necessitates a collaborative effort between federal, state, and local governments, as well as the private sector and individual citizens. The future of coastal communities depends on our collective ability to adapt to a changing climate and build a more resilient future. For further details and access to the map, please visit [ https://www.fema.gov/ ].
Read the Full The Cool Down Article at:
[ https://www.yahoo.com/news/articles/federal-map-reveals-looming-threat-033000819.html ]











